The speciation plot for any conjugate acid-base pair is determined using the expression for the acid’s ionization constant, Ka. We will use acetic acid (CH3COOH) as an example. Acetic acid reacts with water in the following acid-base reaction:
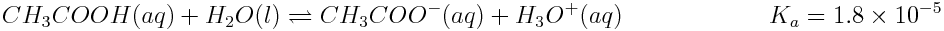
The expression for acetic acid’s ionization constant is:
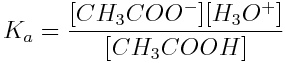
This equation can be rearranged to give:
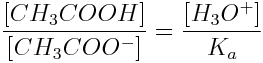
Using this equation and the Ka value for acetic acid, the ratio of acetic acid to acetate ions (CH3COO-) can be calculated for any concentration of hydronium ions and, subsequently, for any pH. For instance, if [H3O+]=1.8×10-2 mol L-1 and pH=1.74, the [CH3COOH]/[CH3COO-] ratio is:
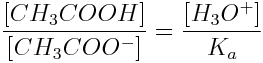


To make a speciation plot, the ratio of [CH3COOH]/[CH3COO-] is experimentally determined at many different pH values. However, speciation plots can also be calculated from equilibrium constants. The relative concentrations of CH3COOH and CH3COO- are expressed as percentages of the total species present in the solution at each pH, and this is plotted on a speciation curve similar to the one shown on the previous page.