Why Should We Care?
Using the Brønsted-Lowry model, we can understand how changes in atmospheric carbon dioxide alter the production of acids in the ocean. Carbon dioxide dissolves in the ocean and then reacts with water, in the following reaction.
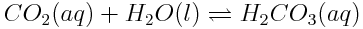
As you saw in the previous worked example, H2CO3(aq)will then act as an acid, donating a proton to a water molecule in the reaction shown below.
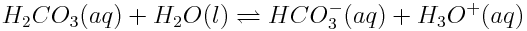
The product of this reaction, HCO3-(aq), can also act as an acid, donating a proton to another water molecule as shown in the reaction below.
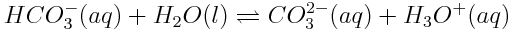
These reactions indicate that atmospheric carbon dioxide can contribute to the production of acids in the ocean.