As the reaction between hydrogen gas and iodine gas proceeds, H2(g) and I2(g) react. As a result, the concentrations of H2(g) and I2(g) decrease while the concentration of HI(g) increases.
Your Turn
Using the reaction quotient, chemists quantitatively describe the relationship between the concentration of reactants and products as reaction proceeds toward equilibrium. Consider the reaction between hydrogen gas and iodine gas:
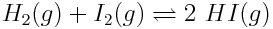
If [H2]=0.0150 mol L-1, according to the stoichiometry of the reaction, [I2] also drops to 0.0150 mol L-1 and [HI] increases to 0.0050 mol L-1. What is the reaction quotient, at this point in the reaction?
The reaction quotient at this point in the reaction is:
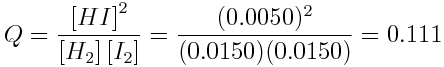
After allowing some time for the reaction to take place, the concentrations of the reactants and products are essentially unchanging. Experimental measurements indicate that [H2]=[I2]=0.0037 mol L-1 while [HI]=0.0276 mol L-1. At this point:
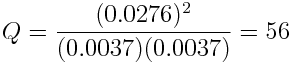
Because the concentrations of the reactants and products are no longer changing, the reaction has reached equilibrium.