What Do We Know?
The strengths of bases are analogous to the strengths of acids. Strong bases are strong electrolytes in solution. Reactions of strong bases in water produce hydroxide ions. For example, NaOH is a strong base that ionizes completely in water:
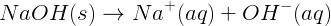
Weak bases, however, do not react completely in aqueous solutions, when they undergo acid-base reactions with water to produce hydroxide ions. Ammonia (NH3), for example, is a weak base and does not react completely with water. Only small amounts of products are formed in this reaction:
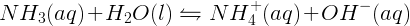
With a pH meter, chemists measure hydronium ion concentrations in aqueous acidic or basic solutions. This concentration indicates the extent of reaction of the acid or base, which enables chemists to classify the acid or base as strong or weak.